

What is a biodegradable polymer?
The term “biodegradable” is said of a substance that may, through living micro-organisms in a natural environment (such as bacteria, fungi, and algae), decompose into various residues such as water, carbon dioxide, methane, mineral salts and a new, non-toxic biomass (humus).
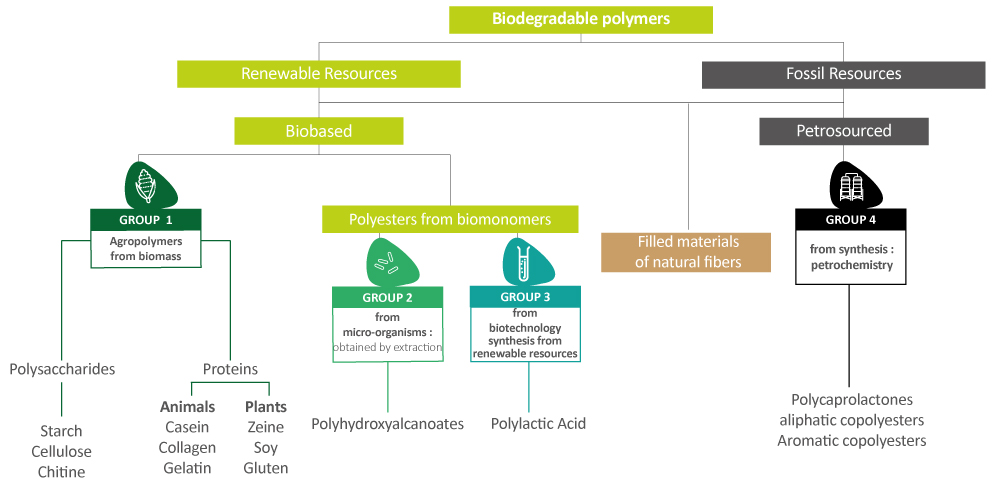
Biodegradable polymers are not necessarily manufactured using renewable raw materials. They can also be derived from fossil resources.
Find Out More
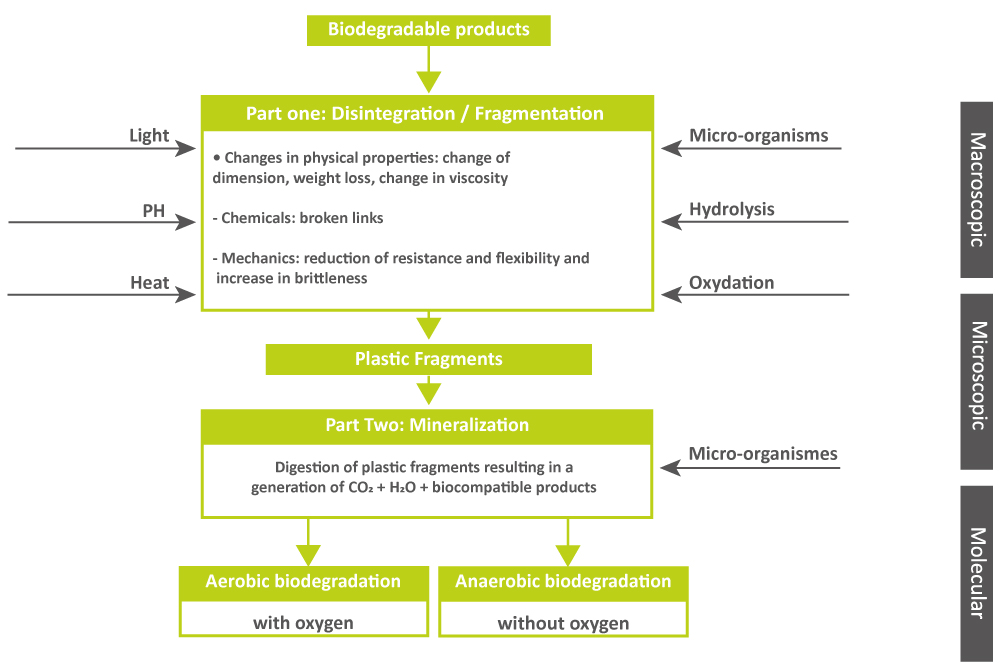
The mechanisms and kinetics of biodegradation are complex; understanding them is essential to gaining a better grasp of the issues surrounding biodegradable polymers. Biodegradation is, in fact, influenced by physicochemical parameters as well as the environment in which it takes place.
million tons is the world share that should represent the production of biodegradable plastics in 2024 according to European Bioplastique.
Understanding the biodegradation
process

Find Out More
The mechanisms and kinetics of biodegradation are complex; understanding them is essential to gaining a better grasp of the issues surrounding biodegradable polymers. Biodegradation is, in fact, influenced by physicochemical parameters as well as the environment in which it takes place.
It should be noted that plastic matter qualified as being “oxo-degradable” or “fragmentable” cannot be classified in the bioplastics category.
Standards regulate and define the characteristics that a material must possess in order to be considered as being biodegradable.
Biodegradable polymer families
Two possible evaluation methods depending on the environment
The biodegradability and compostability of any matter depend on the environment in which it deteriorates. Each environment, be it compost, soil, water or sea, has different temperatures and micro-organisms; the speed of the biodegradation process will vary from an environment to another!
Biodegradable in soil – NF EN 17033

- Temperature : ± 23°C
- Sample : end product
- Biodegradation : <24 mois
with a Tx CO2 > 90% (C -> CO2) - Ecotoxicity
Biodegradable the sea – ISO DIS 22403

- Temperature : depends on the marine environment
- Sample: end product
- Biodegradation : depends on the marine environment temperatures
Biodégradable en compost
- Industrial : NF EN 13432

- Household : NF T51-800

