

What is a bio-sourced polymer?
A bio-sourced polymer is derived entirely or in large part from renewable resources.
Being bio-sourced implies the presence of isotope carbon-14 (C14) within the polymer. It is the C14 concentration within a material that will determine the rate of bio-sourced material.
Unlike bio-sourced polymers, conventional plastics derived from fossil resources that are many millions of years old no longer contain isotope C14 in their macromolecular structure.
Did you know?
Unlike the terms “biodegradable” and “compostable”, which refer to end-of-life management, the term “bio-sourced”, rather, is linked to the origin of the bioplastic resource. The polymer molecules are derived from plants obtained through carbohydrates such as sugar and starch, as well as protein, cellulose, lignin, and bio-fats. Bio-sourced polymers are not necessarily biodegradable.
According to data published by European Bioplastics, the world capacity for the production of bioplastics would require less than 0.02% of the world agricultural area in 2016.
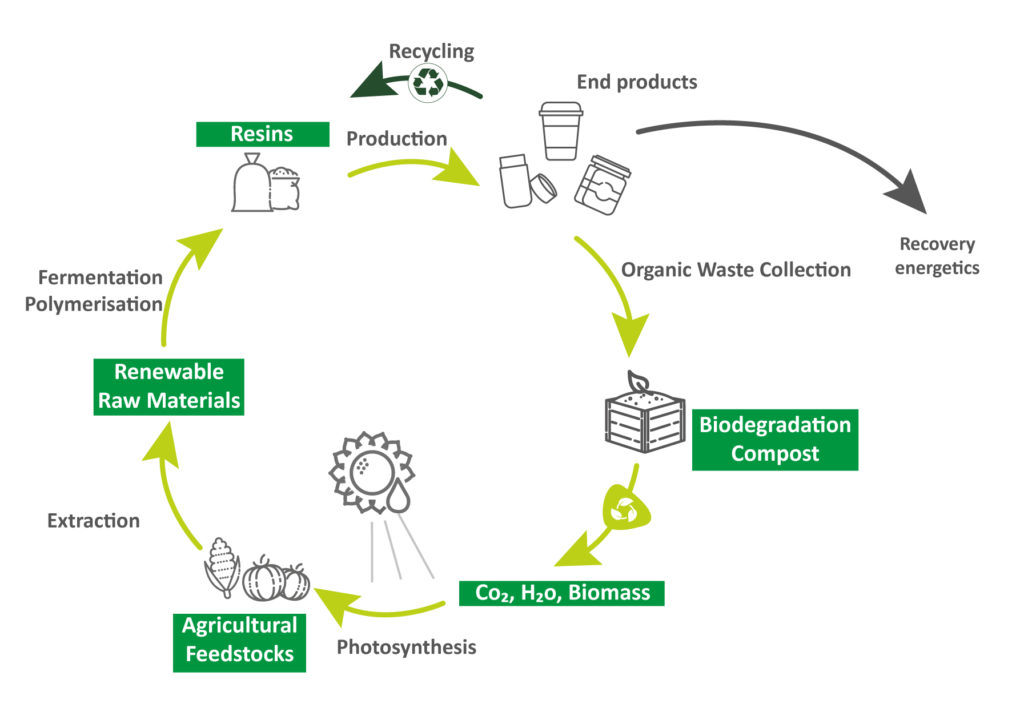
Carbon cycle present in bio-sourced plastics
Bio-sourced polymers are derived from biomass and natural resources whose stock can rebuild itself over a short period of time at human scale and which contains carbon-14 traces (conversely, fossil resources are derived from oil).

Find out more
Bio-sourced plastics can come from diverse resources derived from biomass. Whereas certain bio-sourced polymers can directly compete with feed crops and human nutrition, other types of bio-sourced polymers are derived from co-products or micro-organisms and therefore enable the valorisation of this biomass. It should be noted that bio-sourced polymers are not necessarily biodegradable.
Standards frame and define the characteristics of bio-sourced materials with a % of renewable resources.
Two possible evaluation methods for certification
Evaluation method of the percentage of renewable material contained in the product through carbon-14 dating (radioactivity of C14):
- ASTM D6866: “Standard Test Methods for Determining the Biobased Content of Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous Samples Using Radiocarbon Analysis”
- DIN SPEC 91236 (CEN/TS 16137) : “Plastics – Determination of biobased carbon content”
- ISO 16620 : “Plastics – Biobased content”
Evaluation method of the bio-sourced content taking into account biomass as a whole:
- EN 16785-1 : Determination of biobased content using radiocarbon (C14) and elemental analysis (H,N,O)
